Red Tide Phenomenon Threatens Aquatic Ecosystems
Expert Warns of Potential Marine Devastation
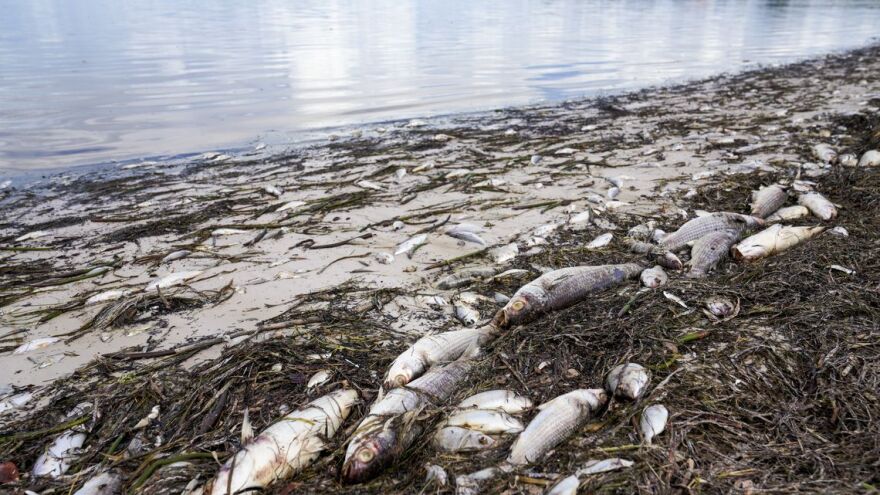
A recent surge in red tide occurrences has raised serious concerns about the health of marine ecosystems in the Gulf of Thailand. The phenomenon, characterized by a rapid increase in certain plankton species, poses a significant threat to aquatic life and local industries.
Seasonal Pattern of Harmful Algal Blooms
Oxygen Depletion Risks Marine Biodiversity
According to Natthawadee Bantiwiwatkul, director of the marine research center, the red tide phenomenon typically occurs from February to April and October to December each year. These plankton blooms can drastically reduce oxygen levels in the water, potentially leading to mass fish deaths and disrupting the delicate balance of marine ecosystems.
Historical Context and Geographic Spread
Coastal Regions Face Recurring Challenges
Reports of red tide occurrences have been documented in various coastal provinces, including Prachuap Khiri Khan and Chumphon from 2019 to 2024, and in Surat Thani from 2011 to 2024. This widespread and persistent nature of the phenomenon underscores the need for comprehensive monitoring and management strategies.
Impact on Local Industries and Tourism
Authorities Urge Caution and Vigilance
The center has called upon relevant agencies to closely monitor the situation, advising tourism operators and locals to avoid water activities to prevent potential skin irritation. Aquatic farmers are also warned to remain vigilant, as the red tide phenomenon can lead to significant losses in fish populations.
Scientific Understanding and Future Outlook
Research Efforts Aim to Mitigate Red Tide Effects
While red tides are natural occurrences, their frequency and intensity may be exacerbated by various factors, including pollution and climate change. Ongoing research aims to better understand the dynamics of these harmful algal blooms and develop effective strategies to mitigate their impact on marine ecosystems and coastal communities.